Java Basic Syntax
import package
class <classname>
{
Public static void main(String args[])
{
//Statement;
}
}
A Java file can contain the following elements:
- Package declaration
- Import statements
- Type declaration
- Fields
- Class initializers
- Constructors
- Methods
When we consider a Java program, it can be defined as a collection of objects that communicate via invoking each other's methods. Let us now briefly look into what do class, object, methods, and instance variables mean.
- Object - Instance of the class is called Object.
- Class - Collection of data members, constructors, and methods is called class.
- Methods - A method is basically a behavior. A class can contain many methods. It is in methods where the logic is written, data is manipulated and all the actions are executed.
- Instance Variables - Each object has its unique set of instance variables. An object's state is created by the values assigned to these instance variables
Popular Java Editors
To write your Java programs, you will need a text editor. There are even more sophisticated IDEs available in the market. But for now, you can consider one of the following:
Notepad: On Windows machine, you can use any simple text editor like Notepad
Netbeans: A Java IDE that is open-source and free, which can be downloaded from
http://www.netbeans.org/index.html.
Eclipse: A Java IDE developed by the Eclipse open-source community and can be downloaded from
http://www.eclipse.org/.
First java program
class HelloWorld
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Helllo World");
System.out.println("Helllo World");
}
}
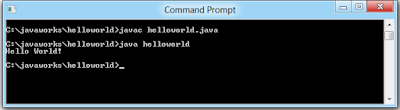
How to save the file, compile, and run the program. Please follow the subsequent steps:
> Open notepad and add the code as above.
> Save the file as helloworld.java.
Classname and program name must be same.
Open a command prompt window and go to the directory where you saved the class.
About Java programs, it is very important to keep in your mind the following points.
Case Sensitivity - Java is case sensitive, which means identifier Hello and hello would have the different meaning in Java.
Class Names - For all class names, the first letter should be in Upper Case. If several words are used to form a name of the class, each inner word's first letter should be in Upper Case.
Example: class Demo
Method Names - All method names should start with a Lower Case letter. If several words are used to form the name of the method, then each inner word's first letter should be in Upper Case.
Example: public void ABC()
Program File Name - Name of the program file should exactly match the class name. When saving the file, you should save it using the class name (Remember Java is case sensitive) and append '.java' to the end of the name (if the file name and the class name do not match, your program will not compile).
Example: Assume 'MyFirstJavaProgram' is the class name. Then the file should be saved as 'MyFirstJavaProgram.java'.
Why we write public static void main(String args[])
Static: is a keyword which identifies the class related thing. This means the given Method or variable is not instance related but Class related. It can be accessed without creating the instance of a Class.
Void: is used to define the Return Type of the Method. It defines what the method can return. Void means the Method will not return any value.
main: is the name of the Method. This Method name is searched by JVM as a starting point for an application with a particular signature only.
String args[]: is the parameter to the main Method.
What is System.out.println?
System.out.println is a Java statement that prints the argument passed, into the System.out which is generally stdout.
- System – is a final class in java.lang package. As per Javadoc, “…Among the facilities provided by the
System class are standard input, standard output, and error output streams; access to externally defined properties and environment variables; a means of loading files and libraries; and a utility method for quickly copying a portion of an array…“
- out – is a static member field of System class and is of type PrintStream. Its access specifiers are public final. This gets instantiated during startup and gets mapped with standard output console of the host. This stream is open by itself immediately after its instantiation and ready to accept data.
- println – is a method of PrintStream class. println prints the argument passed to the standard console and a newline. There are multiple println methods with different arguments (overloading). Every println makes a call to the method
print and adds a newline. print Calls and thewrite() story go on like that.
System class are standard input, standard output, and error output streams; access to externally defined properties and environment variables; a means of loading files and libraries; and a utility method for quickly copying a portion of an array…“print and adds a newline. print Calls and thewrite() story go on like that.